Information about the Parathyroid Glands
Individuals with parathyroid gland disorders may not exhibit any symptoms at all or symptoms will be subtle enough that the problem will go undetected. Fatigue is a common symptom of hyperparathyroidism, especially when accompanied with other symptoms associated with the disorder. For instance, if you have also developed kidney stones in addition to experiencing fatigue, it is a good idea to talk with a doctor about your symptoms.
Since hyperparathyroidism causes an overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and raised calcium levels, a side effect is often kidney stones. Many people discover that they have this condition during a routine blood test when an elevated calcium level is detected. This is why regular checkups are so important, especially since the disorder does not improve on its own and almost always requires surgery.
How to identify parathyroid gland disorders
 Increased anxiety that cannot be explained is another symptom. High blood pressure and other heart-related symptoms is a very common symptom among people with these disorders. An elevated heart rate, palpitations, or arrhythmia are signs that have been observed in people with hyperparathyroidism.
Increased anxiety that cannot be explained is another symptom. High blood pressure and other heart-related symptoms is a very common symptom among people with these disorders. An elevated heart rate, palpitations, or arrhythmia are signs that have been observed in people with hyperparathyroidism.
What are the parathyroid glands
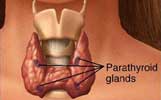 These glands are four pea-sized glands located on the thyroid gland in the neck. Occasionally one or more of the glands are embedded in the thyroid, in the thymus, or located elsewhere around this area – in most such cases, however, the glands function normally. In man, they number four as a rule. Fewer than four were found in less than 1 per cent, but more than four in over 33 per cent. In addition, numerous minute islands of tissue may be found scattered in the connective tissue and fat of the neck around the glands proper, and quite distinct from them.
These glands are four pea-sized glands located on the thyroid gland in the neck. Occasionally one or more of the glands are embedded in the thyroid, in the thymus, or located elsewhere around this area – in most such cases, however, the glands function normally. In man, they number four as a rule. Fewer than four were found in less than 1 per cent, but more than four in over 33 per cent. In addition, numerous minute islands of tissue may be found scattered in the connective tissue and fat of the neck around the glands proper, and quite distinct from them.
The function of the parathyroid glands
 As blood flows through the glands, the amount of calcium and Vitamin D in the blood is checked. If the amount of calcium or Vitamin D is low the gland produces PTH, and if the amount of calcium is high the gland stops producing PTH. This is the function of the glands. Through this mechanism, there is minute-to-minute control of the level of calcium in the blood.
As blood flows through the glands, the amount of calcium and Vitamin D in the blood is checked. If the amount of calcium or Vitamin D is low the gland produces PTH, and if the amount of calcium is high the gland stops producing PTH. This is the function of the glands. Through this mechanism, there is minute-to-minute control of the level of calcium in the blood.
Signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism
 A person with hyperparathyroidism may have severe symptoms, subtle ones, or none at all. The commonest finding is an elevated calcium level on a routine blood test. Patients may have thinning of the bones without symptoms. When the signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism do appear, they are often mild and nonspecific, such as a feeling of weakness and fatigue, depression, or aches and pains.
A person with hyperparathyroidism may have severe symptoms, subtle ones, or none at all. The commonest finding is an elevated calcium level on a routine blood test. Patients may have thinning of the bones without symptoms. When the signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism do appear, they are often mild and nonspecific, such as a feeling of weakness and fatigue, depression, or aches and pains.
Parathyroid disorders
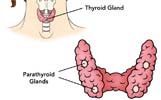 Hyperparathyroidism is one of the parathyroid disorders where the glands makes more of the PTH than the body needs, causing an imbalance in the amount of calcium in the body.This can lead to problems with the bones, muscles, nervous system, and kidneys and is caused by inappropriately increased secretion of PTH.
Hyperparathyroidism is one of the parathyroid disorders where the glands makes more of the PTH than the body needs, causing an imbalance in the amount of calcium in the body.This can lead to problems with the bones, muscles, nervous system, and kidneys and is caused by inappropriately increased secretion of PTH.
Parathyroid diagnosis
 Under normal conditions, a normal calcium level will be associated with a normal PTH level. Also under normal conditions, a low serum calcium level will be associated with a high PTH level; a high calcium level will be associated with a low PTH level. These are all appropriate ways in which the glands will react to calcium that is circulating in the blood as they attempt to regulate calcium in the narrow normal range.
Under normal conditions, a normal calcium level will be associated with a normal PTH level. Also under normal conditions, a low serum calcium level will be associated with a high PTH level; a high calcium level will be associated with a low PTH level. These are all appropriate ways in which the glands will react to calcium that is circulating in the blood as they attempt to regulate calcium in the narrow normal range.
Parathyroid disorder treatment
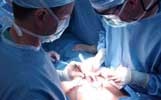 If one or more of the parathyroid glands are overactive there are two types of treatment. Traditional parathyroid surgery – Open Parathyroidectomy or Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy. Surgery to remove the enlarged gland (or glands) is the main treatment for the disorder and cures up to 98 percent of patients – most patients feel better as early as 72 hours after surgery.
If one or more of the parathyroid glands are overactive there are two types of treatment. Traditional parathyroid surgery – Open Parathyroidectomy or Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy. Surgery to remove the enlarged gland (or glands) is the main treatment for the disorder and cures up to 98 percent of patients – most patients feel better as early as 72 hours after surgery.
Open Parathyroidectomy
 Open surgery is the traditional treatment of choice for people with primary hyperparathyroidism. This surgery cures fatigue and the bone, abdominal, urological, and mental symptoms associated with hypercalcaemia.
Open surgery is the traditional treatment of choice for people with primary hyperparathyroidism. This surgery cures fatigue and the bone, abdominal, urological, and mental symptoms associated with hypercalcaemia.
Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy (MIP)
 MIP involves a small incision on one side of the neck – it is done when one abnormal gland is identified on preoperative testing.
MIP involves a small incision on one side of the neck – it is done when one abnormal gland is identified on preoperative testing.
If you have questions about the parathyroid glands, contact your local doctor who will arrange for you to see a thyroid surgeon.

