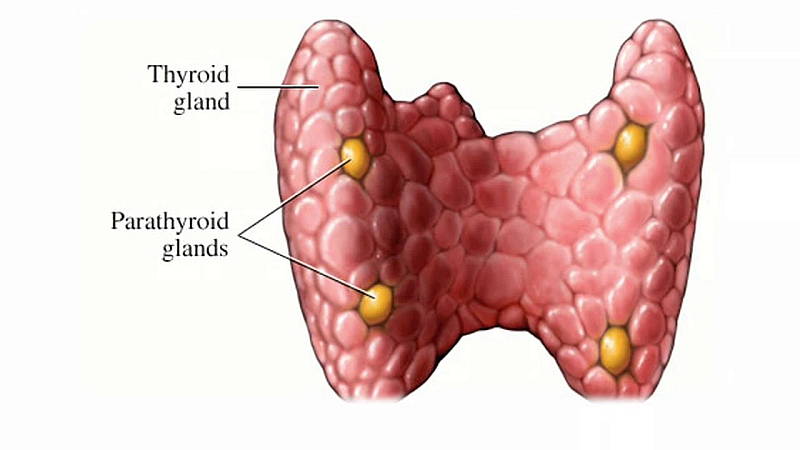
The parathyroid glands are located behind the thyroid, in your neck. Hypoparathyroidism is a condition where the body does not produce sufficient parathyroid hormone or PTH.
PTH is responsible for the regulation of phosphorus and calcium levels in your body. This is circulated in your blood and stored in your bones. PTH directly affects your body’s reservoir of calcium within your bones. It will also tell your kidneys to secrete or retain calcium, and will work together with vitamin D in controlling the calcium absorbed from your diet.
Decreased PTH levels lead to high phosphorus levels and low calcium levels in your blood. The imbalance may lead to issues with skin, nerve endings, muscles and bones.
What are the symptoms of hypoparathyroidism?
Hypoparathyroidism symptoms may include:
- Coarse, dry skin, brittle nails and dry hair
- Tingling in your fingers, lips and toes
- Cataracts
- Muscle cramps
- Malformation of teeth
- Calcium deposits in the kidney or brain
- Memory loss
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Severe muscle spasms, sometimes leading to convulsions
How is hypoparathyroidism diagnosed?
Your doctor will use blood tests to determine the following blood levels:
- Phosphorus
- Calcium
- Parathyroid hormone
- Magnesium
- Creatinine
- 25-hydroxy vitamin D1
Your physician may also test urine to find out the amount of calcium your body is excreting.
Can hypoparathyroidism be cured?
There is no cure currently for hypoparathyroidism. If your parathyroid glands are non-functional, or if they were removed in the course of thyroid surgery to manage a condition like Graves’ Disease or to remove a tumour, then you will then need to be sure to maintain adequate levels of vitamin D and calcium. This can be done via medication and supplementation.
How can hypoparathyroidism be treated?
The goal in treating this disorder is the restoration of your phosphorus, calcium and magnesium levels in the urine and blood to normal levels. This daily supplementation therapy.
If you have hypoparathyroidism, you may be encouraged by your doctor to eat foods or drink juices that are high in calcium. These include green, leafy vegetables, fortified orange juice, breakfast cereal and dairy products.
Hypoparathyroidism is not treated by supplying the body with the hormone that is missing. However, several experimental research studies have been done with various types of parathyroid hormone. For more than two decades, researchers conducting this study have been providing and evaluating a synthetic parathyroid hormone, known as PTH 1-34, for use in severe cases of hypoparathyroidism. This study examines the long-term effects of PTH therapy on calcium metabolism, bone, and renal function.
Are there complications in hypoparathyroidism its treatments?
If you have the congenital form of hypoparathyroidism and you are diagnosed early and promptly treated, your outcome will usually be good. The body tends to grow normally when this is the case.
If you have untreated hypoparathyroidism, you may experience complications that include:
- Severe muscle spasms that can lead to a blocked airway
- Malformed or poorly formed teeth
- Severe muscle spasms
- Stunted growth
- The development of calcium deposits in the brain
- The development of cataracts
Overtreatment of hypoparathyroidism may cause problems. Replacing too much vitamin D and calcium may cause a higher than normal blood calcium level leading to problems with the kidneys. This is known as hypercalcemia. In severe cases this may lead to tissue damage and reduced function. Uncommonly, hypoparathyroidism treatment may lead to a failure in the kidneys, caused by a calcium buildup. This is called nephrocalcinosis. This type of build-up may or may not be associated with hypercalcemia, and it can occur even if the calcium levels in your blood are within normal range. Careful management is required with the guidance of an Endocrinologist
If you have questions or concerns about the hypoparathyroidism contact your local doctor, who will arrange for you to see an Endocrinologist.
For more information about research for hypoparathyroidism click here.

